File size: 7,502 Bytes
73c95a1 81468ae 73c95a1 81468ae 73c95a1 2bf3130 81468ae 73c95a1 a464e0f 73c95a1 81468ae 2d2c4dd |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 |
---
library_name: transformers
tags:
- reward
- RM
- Code
- AceCode
- AceCoder
license: mit
datasets:
- TIGER-Lab/AceCode-89K
- TIGER-Lab/AceCodePair-300K
language:
- en
base_model:
- Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct
---
# 🂡 AceCoder
[Paper](https://github.com/TIGER-AI-Lab/AceCoder/blob/main/assets/pdf/acecoder_v1.pdf) |
[Github](https://github.com/TIGER-AI-Lab/AceCoder) |
[AceCode-89K](https://huggingface.co/datasets/TIGER-Lab/AceCode-89K) |
[AceCodePair-300K](https://huggingface.co/datasets/TIGER-Lab/AceCodePair-300K) |
[RM/RL Models](https://huggingface.co/collections/TIGER-Lab/acecoder-67a16011a6c7d65cad529eba)
We introduce AceCoder, the first work to propose a fully automated pipeline for synthesizing large-scale reliable tests used for the reward model training and reinforcement learning in the coding scenario. To do this, we curated the dataset AceCode-89K, where we start from a seed code dataset and prompt powerful LLMs to "imagine" proper test cases for the coding question and filter the noisy ones. We sample inferences from existing coder models and compute their pass rate as the reliable and verifiable rewards for both training the reward model and conducting the reinforcement learning for coder LLM.
**This model is the official AceCodeRM-7B trained from Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct on [TIGER-Lab/AceCodePair-300K](https://huggingface.co/datasets/TIGER-Lab/AceCodePair-300K)**
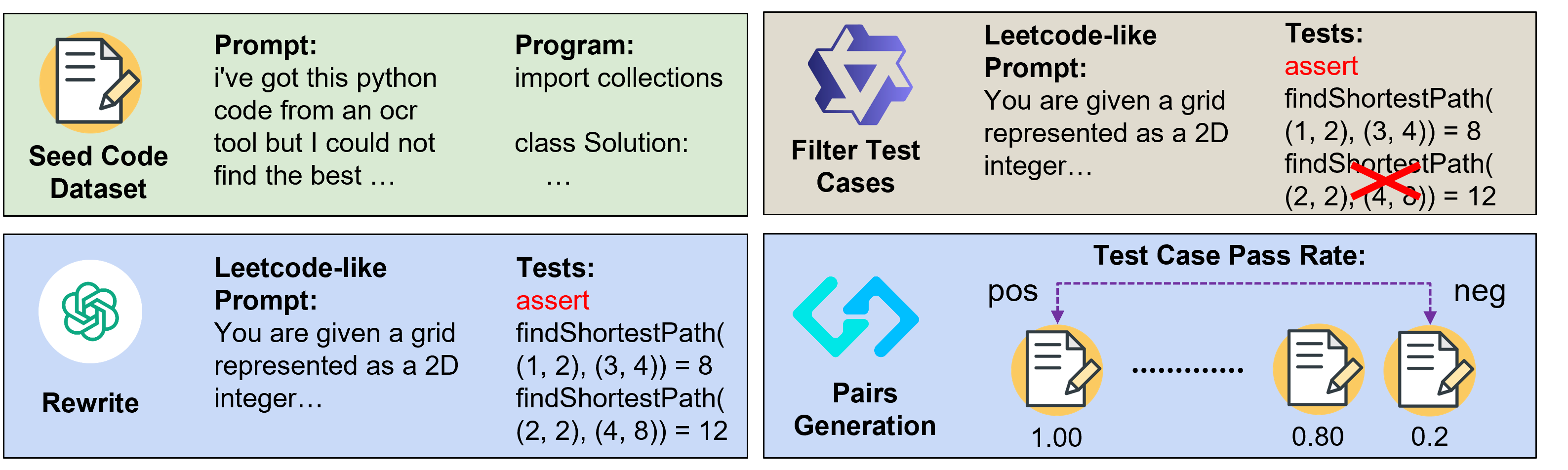
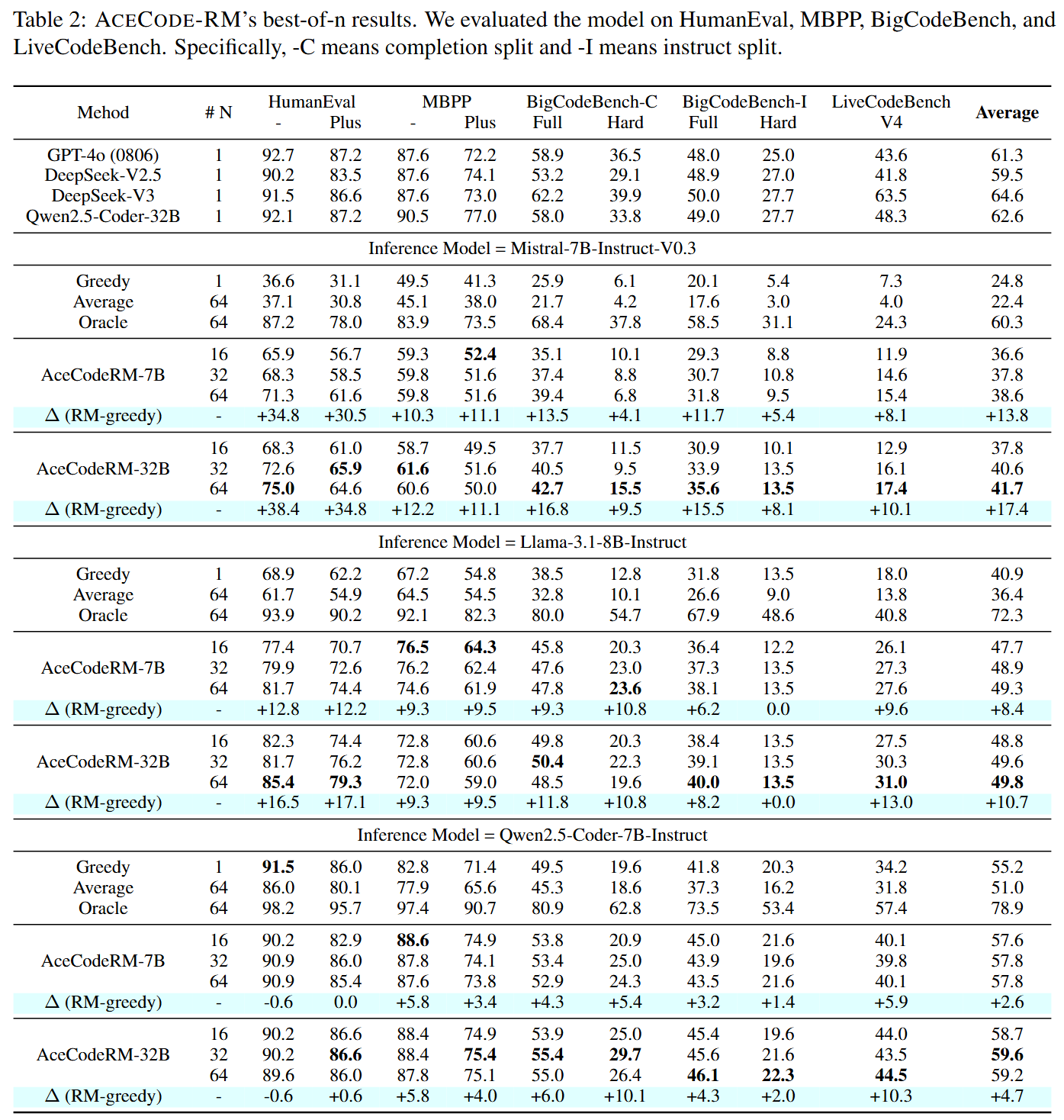
## Performance on Best-of-N sampling
## Usage
- To use the RM to produce rewards, please apply the following example codes:
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from transformers import Qwen2ForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
class ValueHead(nn.Module):
r"""
The ValueHead class implements a head for GPT2 that returns a scalar for each output token.
"""
def __init__(self, config, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
if not hasattr(config, "summary_dropout_prob"):
summary_dropout_prob = kwargs.pop("summary_dropout_prob", 0.1)
else:
summary_dropout_prob = config.summary_dropout_prob
self.dropout = (
nn.Dropout(summary_dropout_prob) if summary_dropout_prob else nn.Identity()
)
# some models such as OPT have a projection layer before the word embeddings - e.g. OPT-350m
if hasattr(config, "hidden_size"):
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
if hasattr(config, "word_embed_proj_dim"):
hidden_size = config.word_embed_proj_dim
elif hasattr(config, "is_encoder_decoder"):
if config.is_encoder_decoder and hasattr(config, "decoder"):
if hasattr(config.decoder, "hidden_size"):
hidden_size = config.decoder.hidden_size
self.summary = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
def forward(self, hidden_states):
output = self.dropout(hidden_states)
# For now force upcast in fp32 if needed. Let's keep the
# output in fp32 for numerical stability.
if output.dtype != self.summary.weight.dtype:
output = output.to(self.summary.weight.dtype)
output = self.summary(output)
return output
class Qwen2ForCausalRM(Qwen2ForCausalLM):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.v_head = ValueHead(config)
def forward(
self,
input_ids=None,
past_key_values=None,
attention_mask=None,
return_past_key_values=False,
**kwargs,
):
r"""
Applies a forward pass to the wrapped model and returns the logits of the value head.
Args:
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary.
past_key_values (`tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor))`, `optional`):
Contains pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the attention blocks) as computed by the model
(see `past_key_values` input) to speed up sequential decoding.
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, `optional`):
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in ``[0, 1]``:
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
return_past_key_values (bool): A flag indicating if the computed hidden-states should be returned.
kwargs (`dict`, `optional`):
Additional keyword arguments, that are passed to the wrapped model.
"""
kwargs["output_hidden_states"] = (
True # this had already been set in the LORA / PEFT examples
)
kwargs["past_key_values"] = past_key_values
# if (
# self.is_peft_model
# and
# self.pretrained_model.active_peft_config.peft_type == "PREFIX_TUNING"
# ):
# kwargs.pop("past_key_values")
base_model_output = super().forward(
input_ids=input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
**kwargs,
)
last_hidden_state = base_model_output.hidden_states[-1]
lm_logits = base_model_output.logits
loss = base_model_output.loss
if last_hidden_state.device != self.v_head.summary.weight.device:
last_hidden_state = last_hidden_state.to(self.v_head.summary.weight.device)
value = self.v_head(last_hidden_state).squeeze(-1)
# force upcast in fp32 if logits are in half-precision
if lm_logits.dtype != torch.float32:
lm_logits = lm_logits.float()
if return_past_key_values:
return (lm_logits, loss, value, base_model_output.past_key_values)
else:
return (lm_logits, loss, value)
model_path = "TIGER-Lab/AceCodeRM-7B"
model = Qwen2ForCausalRM.from_pretrained(model_path, device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, trust_remote_code=True)
input_chat = [
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!",
},
]
input_tokens = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
input_chat,
tokenize=True,
return_dict=True,
padding=True,
return_tensors="pt",
).to(model.device)
_, _, values = model(
**input_tokens,
output_hidden_states=True,
return_dict=True,
use_cache=False,
)
masks = input_tokens["attention_mask"]
chosen_scores = values.gather(
dim=-1, index=(masks.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True) - 1)
) # find the last token (eos) in each sequence, a
chosen_scores = chosen_scores.squeeze()
print(chosen_scores)
```
- To use the RM for the RL tuning, please refer to our [Github Code](https://github.com/TIGER-AI-Lab/AceCoder) for more details
## Q&A
If you have any questions, please feel free to shoot us an email. |